Overview
This activity will take place over a few weeks. Students will plant seeds, build a shoebox maze, and observe how plants grow toward the light.
Instructions
What you'll need
Two weeks before full activity - plant seeds and allow them to sprout above soil:
- Bean seeds
- Soil (enough for class to fill 1 pot each)
- Small pots (1 per student)
- Access to artificial light (e.g. LED light bulb) and natural light from a window
Activity day
For each group (3-4 students):
- 1 shoebox
- 1 set of tape and scissors
- Extra cardboard
For classroom:
- “Light maze” slideshow
Sprouting the beans (two weeks before full activity)
- Explain to the students they'll be growing bean plants, making a shoebox maze and learning how plants grow toward the light.
- Divide the students into groups of three to four. Ask them to name their group something to do with light and/or plants.
- Provide each group with three to four small pots (one per student), put the name of their group on each pot, and fill the pots with soil nearly to the top. Push one seed per pot into the soil about 1 cm deep. Gently push the soil over the seed.
- Ask the students to share what plants need to grow, like water, warmth and light. Have the students share what light sources are available in the classroom. There needs to be natural light from a window and artificial lights that are powered by electricity (LED or compact fluorescent lights at a safe distance from the box to avoid over heating).
- Ask the students to place their pots under one of the light sources. Explain to each group that they are responsible each day for making sure that the soil is damp (not saturated with water). If necessary, use a chart to check each day. Turn off the artificial light at night. When the seeds start to sprout (about 8-14 days), you are ready for the next stage of the project.
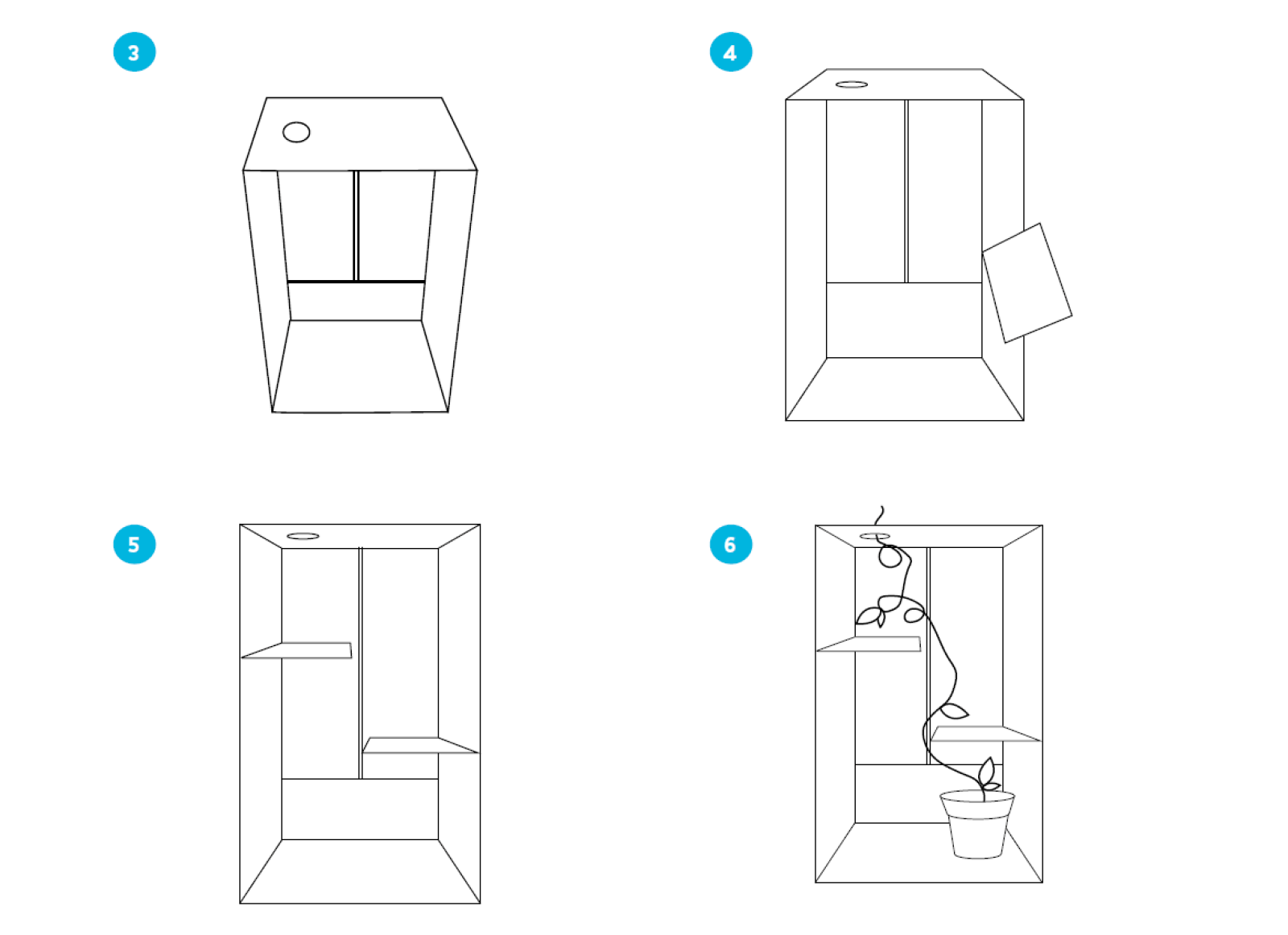
Building the maze
- Make sure each group has 1 shoebox, tape, scissors, and extra cardboard.
- Ask each group to find their sprouted bean pots and choose the strongest plant (It is possible that some of the beans will not have sprouted).
- Pull up the “Light maze” slideshow.
- Explain to the students that they are building a maze for their plants to demonstrate how plants grow towards the light. Slide 2 shows the finished maze and an example of a mature plant growing towards the light.
- Follow the slides to build the maze, place the plant inside, cover the front with the lid and have half the groups place the box under a natural light source, and half under an artificial light source (optional to have multiple types of artificial lights).
- Each group is responsible for taking care of their bean plant. Each group should remove the lid every day to check if the plant needs water and note the differences in the plant growth.
- Discuss with the students the following questions:
- What do students think will happen?
- How will the bean plant grow?
- Which of the lights will work best?
- As the plant grows, have the students note the following:
- How does the bean plant change each day?
- Have the students compare notes with other groups
- Which bean plants are doing better than others?
- Once the plant grows through the hole in the top of the shoebox, ask the students to report on the following:
- What happened?
- Did all of the bean plants survive?
- Which of the lights worked best?
- What was the bean plant doing?
- Why might we choose natural light instead of artificial light?
- How can using natural light help us to conserve energy?
- Why might we choose to use artificial light?
Modify or extend this activity
- Create a graph to track the growth of the plant over time.
- In the spring, construct a mini outdoor garden with a trellis for the bean plants to continue growing towards the light.
Curriculum Fit
Grade 5 Social Studies
Big ideas and content
- Natural resources continue to shape the economy and identity of different regions of Canada.
Grade 5 Science
Content
- Nature of sustainable practices around B.C.’s resources.
Curriculum competencies
Questioning and predicting
- Demonstrate a sustained curiosity about a scientific topic or problem of personal interest and make predictions about the findings of their inquiry.
Planning and conducting
- Observe, measure, and record data, using appropriate tools, including digital technologies.
Processing and analyzing data and information
- Experience and interpret the local environment.
Grade 5 Mathematics
Content
- Data represented in graphs can be used to show many-to-one correspondence.
Assessments
- Assess students’ understanding of the basic needs of plants, including water and light.
- Assess students’ ability to work collaboratively and follow instructions to plant the seed, nurture and care for the plant and build the shoebox maze.
- Assess students’ communication and cooperation in groups.
Teaching Notes
Plants move
Their roots grow down (or laterally) and the aerial parts grow towards natural or artificial light. The process of photosynthesis uses light energy to turn carbon dioxide and water into sugars, which the plant uses. Essentially, the plant needs to find light to get food.
Natural versus artificial light
Although plants will grow under artificial light, studies have shown that they prefer natural light which has a perfect balance of wavelengths necessary for plant growth. Use of artificial light (greenhouses and in underground spaces) is a growing industry. Benefits include the ability to grow local food throughout the year, however, there are impacts on energy, and light pollution.
Natural light can benefit our health and save energy.
Natural light:
- Helps improve mental health
- Improves sleep
- Increases ability to concentrate and learn
- Helps our bodies to produce vitamin D which help us build and maintain teeth and bones and absorb calcium
- Saves energy as we can turn off the artificial lighting
Keep blinds or curtains open to let in natural light during the day instead of turning on the lights.
LED lighting
LED light bulbs have a long lifetime and use 75% less energy than incandescent light bulbs. There is also a range of colours available for LED bulbs, ranging from a soft yellow to a bright daylight, which can provide an alternate to natural light. Go to bchydro.com for more information on LED lighting.






