Overview
Sounds are everywhere. Make a homemade kazoo to hear, see, and feel vibrations. Students will earn the differences between natural and artificial sounds.
Instructions
What you'll need
- Laptop and projector
- "See, hear, feel sound" slideshow
- "Kazoo craft" instructions
Kazoo craft
Prepare an example of the kazoo craft before class. This is beneficial because it shows the students exactly what they are expected to do.
- Materials per student
- paper towel or toilet paper roll tube
- 1 pre-cut square of wax paper (4’ x 4’)
- elastic band
- markers / colouring materials
- scissors / pen (something to poke a hole into the kazoo)
- For the class demonstration
- 1 bowl (steel or porcelain)
- 1 sheet of plastic wrap (big enough to cover the bowl tightly)
- Salt (coloured sprinkles may be used as an alternative, if available)
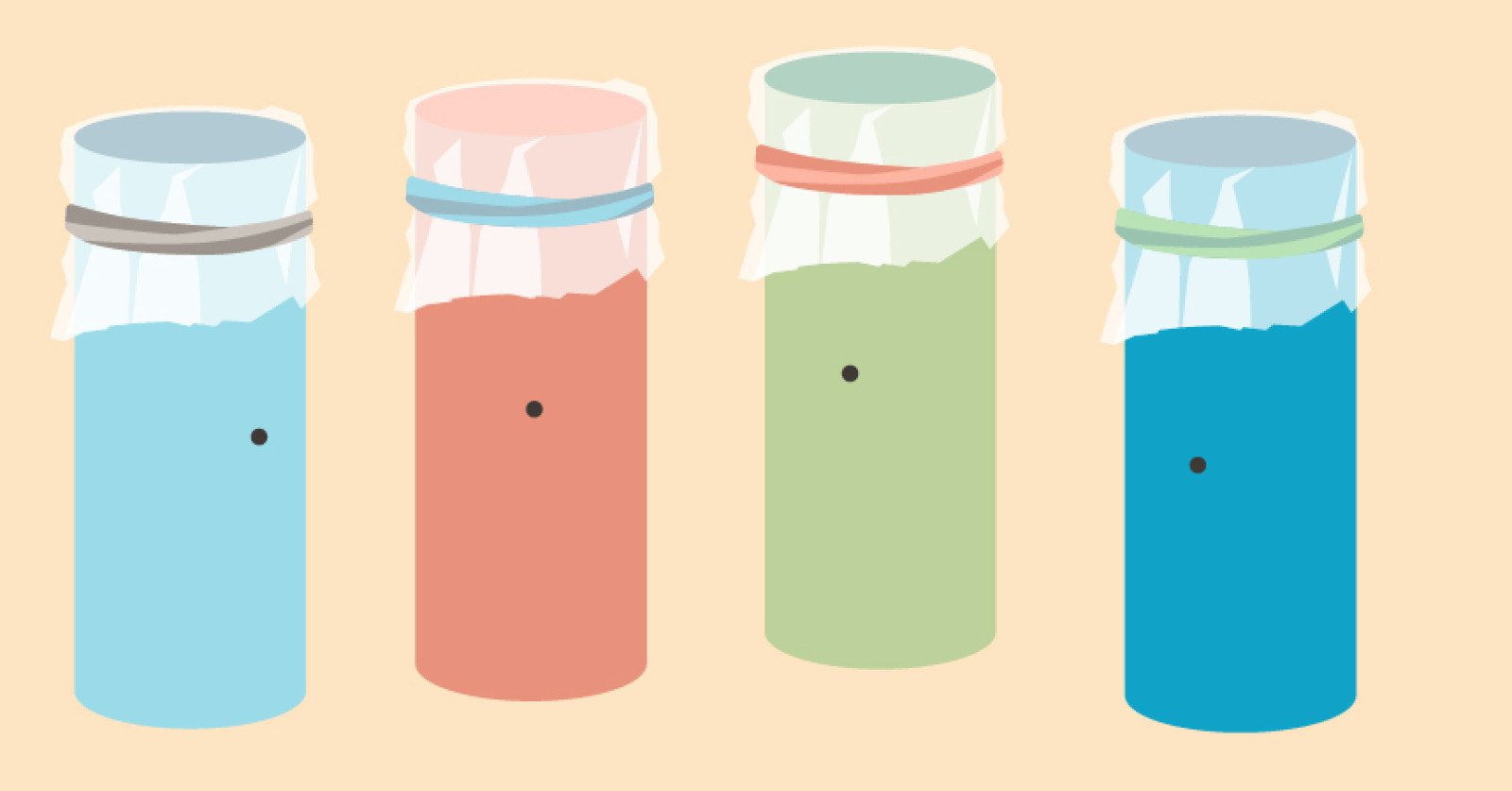
- Stretch plastic wrap tightly over the bowl and secure it with a rubber band. Make sure the plastic wrap is smooth and there are no wrinkles. Do not add salt or sprinkles until the class demonstration in front of the students. You can refer to this video for a visual example.
- Use a laptop and projector to present "See, hear, feel sound" slideshow.
- Start by asking students to think of different sounds that they hear during their everyday lives. In slide 2, you can mention: sound of rain falling, bees buzzing, cars honking, train moving, dogs barking, people talking, sirens wailing, phones ringing.
- In slides 3-5, explain that some sounds are natural and some sounds are artificial.
- Natural sounds are found in nature. A few examples: birds chirping, wolf howling, meow of a cat, the bark of a dog, water in the river flowing, people talking, people singing, the sound of rain and thunder.
- Artificial sounds or noises are made by humans. Some examples include cars honking on the street, alarm clocks ringing, phones ringing, music coming from a flute, sounds coming from the speakers of the TV.
- Explain how sound travels in waves and causes vibrations in the inner ear referencing slide 6.
- Ask students to hold their hand over their throat while saying “aaahhhh” or “ohhhhhh” for a long time. Ask them to notice how the “sound” of their voice feels against their hand. Explain that what they’re feeling is a vibration.
- Optional: Show another example of a toy being thrown into a bucket of water. It makes a "splash" sound. You can see the water moving when the sound is made.
- Optional: Show another example of guitar strings being plucked. When the sound is produced, the strings vibrate quickly back and forth.
- The vibrations create sound waves. The sound waves travel through the air, reaches our ears and we are able to hear the sound.
- Have you ever heard of a “slinky” toy? Slinkies are a great way to see how sound waves work.
- Optional: Video that demonstrates how sound travels using a slinky (Source: MightyOwl).
- Close the slideshow presentation. Pull out your kazoo example. Blow into the kazoo and make a sound. It causes a “hum” or “buzzing” feeling against the lips. This “feeling” is a vibration.
- Do a demonstration to show how sound travels in waves. Take out a bowl covered in plastic wrap (prepared in advance). Pour the sprinkles (or salt) on top of the saran wrap. You can reference this video: Vibration and sound (Source: Science buddies). It shows a student “humming” to make the sprinkles move. Instead of this, blow air into the kazoo over the top of the saran wrap to cause the sprinkles (or salt) to vibrate. Sound waves make the plastic wrap vibrate (move very quickly), making the sprinkles “dance”.
- If you don’t see the sprinkles or salt move across the plastic wrap, try moving the kazoo closer to the bowl, or humming louder.
- Explain to students that it’s their turn to make their own kazoo. After they are done, they can try making the sprinkles “dance” across the plastic wrap on the bowl.
Kazoo craft
- Distribute the materials to each student. 1 paper towel tube per student.
- Ask students to spend 15 minutes drawing pictures, colouring, decorating their paper towel tube with their colouring materials.
- Distribute the pre-cut squares of wax paper and 1 rubber band per student.
- Cover the top of the paper towel tube with the wax paper and secure with a rubber band. The wax paper should be tight across the top.
- Poke a small hole into the paper towel tube to allow the sound to escape (use scissors, or a pen/pencil)
- Try blowing into the kazoo (the mouthpiece is opposite from the wax paper end).
- Supervise the students as they blow their kazoo over the bowl. As they’re watching the sprinkles (or salt) “dance” across the saran wrap, ask questions to recall what they learned about vibrations, and sound waves.
- What is happening when we don’t blow on the kazoo?
- When we are not blowing on the kazoo, air is not hitting it.
- There is no vibration.
- Try talking into your kazoo. What happens?
- Air from your mouth moves through the kazoo.
- It causes a vibration to happen.
- What are the sprinkles doing?
- They're vibrating.
- What does vibrating mean?
- Moving very fast.
- How does sound travel?
- Sound travels through the air in the form of sound waves.
- How can our ears hear the sound?
- Air and sound from our voice comes out of our mouth, hits the wax paper on the kazoo, and causes it to vibrate. The sound waves travel through the air and hits our ear, which causes us to hear the sound.
- What is happening when we don’t blow on the kazoo?
Modify or extend this activity
- Make a T chart and label the left side “artificial” sounds and the right side “natural” sounds. Make a class list of artificial sounds that can be heard from the classroom. Take students to a forest, park or nature area where there are only natural sounds to hear. Ask students to listen to natural sounds and add to the class list.
- Ask students to reflect about how they feel when they hear artificial sounds and natural sounds. Ask students if they feel the same or different than Thunder from the story. Ask them to share stories from their personal experiences.
Curriculum Fit
Grade 2 Science
Core competencies: Communication, Thinking
Big ideas
- Materials can be changed through physical and chemical processes.
- Forces influence the motion of an object.
Curricular competencies
Questioning and Predicting
- Demonstrate curiosity and a sense of wonder about the world.
- Observe objects and events in familiar contexts.
- Make simple predictions about familiar objects and events.
Planning and conducting
- Safely manipulate materials to test ideas and predictions.
Processing and analyzing data and information
- Experience and interpret the local environment.
- Recognize First Peoples stories (including oral and written narratives), songs, and art, as ways to share knowledge.
Communication
- Communicate observations and ideas using oral or written language, drawing, or role-play.
- Express and reflect on personal experiences of place.
Grade 3 Science
Core competencies: Communication, Thinking
Big ideas
- Living things are diverse and interact with their ecosystems.
- Interconnectedness means that all things are related to and interact with each other in the environment.
Curricular competencies
Questioning and predicting
- Demonstrate curiosity and a sense of wonder about the world.
- Observe objects and events in familiar contexts.
- Make simple predictions about familiar objects and events.
Planning and conducting
- Make observations about living and non-living things in the local environment.
Applying and Innovating
- Contribute to care for self, others, school, and neighbourhood through personal or collaborative approaches.
Communication
- Represent and communicate ideas and findings in a variety of ways.
- Express and reflect on personal experiences of place.
Assessments
- Assess students’ understanding of natural and artificial sounds around us.
- Assess students’ knowledge of how artificial sounds often use. power and what choices we can make to reduce the sound and conserve energy.
Teaching Notes
Two types of sounds
- Artificial sounds are made by humans. Examples include: a phone ringing, a school bell ringing, an alarm clock ringing, a clock ticking, sirens coming from a police car or ambulance, music coming from a piano (or any instrument).
- Natural sounds are found in nature. Examples include: the human voice, the sound of a human heartbeat, the buzz of a bee, the meow of a cat, the bark of a dog, the moo of a cow, the sound of the ocean waves, the sound of rain hitting a window, the roar of a tiger, birds chirping, the sound of horse hooves on the ground.
- Sound travels through the air in waves. When sound waves “hit” something, it causes the object to move back and forth quickly. This is called a vibration.
- Example: Ask students to hold their hand over their throat while saying “aaahhhh” or “ohhhhhh”. Ask them to notice how the “sound” of their voice feels against their hand. Explain that what they’re feeling is a vibration.
- Sound also travels through water in the form of waves. Animals like whales, dolphins and sharks use sound waves in the water to detect prey and communicate with each other. Sounds used by animals to find food and communicate is called echolocation. Echolocation describes how sound waves hitting an object are reflected back to the animal, to let them know that food is nearby. Dolphins and whales used their tongue to generate a clicking sound. The clicking sound is emitted through the water like waves. When the sound wave hits an object, it is reflected back, and if there are no objects in the way, the wave is not reflected back. This is how some animals in the ocean can find food even when they can’t see their prey.
Sound is an example of both kinetic and potential energy
- Potential energy: Stored energy. An object that is at rest has the ability to do work but is not presently doing so. A ball sitting at the top of a hill and is not moving has only potential energy. The potential energy is converted into kinetic energy as soon as it starts to roll down the hill.
- Kinetic energy: the energy an object has because of its motion. “Moving” energy.
- Example: Think about a musical instrument. When the music is not being played, only the potential energy is present. The musical instrument has the ability to do work but is not presently doing so. When the instrument is played, the potential energy is transformed into kinetic energy. The energy moves through the air in waves, causing the instrument to vibrate.
Making sound more accessible for all
Sounds can be felt when we consider the needs of individuals who may have difficulty hearing sounds. Imagine you're playing a game with your friend who can't hear. To include them, you might stomp your feet on the ground to create vibrations that they can feel through their feet. This is similar to how some individuals who are not able to hear sounds, use vibrations, like a special alarm clock that shakes the bed, to wake up in the morning.