Conservation
Energy source choices
Students research and share how different energy sources impact our environment.

Overview
Discover the many different energy resources we use and their environmental impact.
Instructions
What you'll need
- Print the “Energy choices” student handout, 1 copy per group
- Divide the class into groups, approx. 2-4 students per group and explain they'll be doing a research project on energy resources in B.C.
- Let your students select an energy resource such as hydro, wind, solar, biomass, geothermal, nuclear, coal, oil, natural gas (fossil fuel), renewable natural gas (biofuel) or tidal energy.
- Ask the students to research and present their findings in a way that can be shared with the rest of the class. Some ideas:
- A poster
- An information brochure
- A slideshow presentation
- Provide each group with the “Energy choices” student handout with questions to guide their research.
- Have the students present their findings to the class and have a class discussion on renewable versus non-renewable energy resources.
Modify or extend this activity
Extensions
- Take a look at this video to get a sneak peek inside a B.C. hydroelectric dam.
- Consider the "Introduction to electricity" lesson to further explore energy in B.C.
- Watch the "Our clean energy" video to learn more about renewable and non-renewable energy.
Curriculum Fit
Grade 7 Social Studies
Big idea
- Geographic conditions shaped the emergence of civilizations
Content
- Human responses to particular geographic challenges and opportunities, including climates, landforms, and natural resources
Curricular competencies
- Use Social Studies inquiry processes and skills to — ask questions; gather, interpret, and analyze ideas; and communicate findings and decisions
Grade 7 Science
Big idea
- The electromagnetic force produces both electricity and magnetism
Content
- Electricity: generated in different ways with different environmental impacts
Curriculum competencies
Questioning and predicting
- Demonstrate a sustained intellectual curiosity about a scientific topic or problem of personal interest
Assessments
- Assess the students’ understanding of the energy resource researched.
- Assess the students’ participation in group research and presentation of information.
- Assess the students’ ability to present the pros and cons of energy resources.
Teaching Notes
Canadian energy facts
(Source: Natural Resources Canada)
- Coal: Coal is a mineral deposit rich in carbon. Canada currently exports and imports coal but in 2016, the Government of Canada announced its plan to eliminate the use of traditional coal fired electricity in Canada by 2030
- Oil: Canada is the world’s fourth largest crude oil exporter and 98% of Canada’s proven oil reserves are located in the oil sands
- Natural gas: Canada is the fourth largest producer and fifth largest exporter of natural gas. Natural gas is composed primarily of methane.
- Electricity: 66% of Canada’s electricity comes from renewable sources and 81% from non-GHG emitting sources. Canada is the world’s second largest producer of hydroelectricity.
- Renewable energy: This is generated from solar, wind, biomass, geothermal, hydropower and ocean resources, solid biomass, biogas and liquid biofuels. Wind and solar photovoltaic energy are the fastest growing sources of electricity in Canada.
- Nuclear: Uranium is a metal that is mined, milled, refined, converted, and finally used to fuel nuclear power generation. Canada is the world’s second largest producer and exporter of uranium. Nuclear power plants generate about 15% of Canada’s electricity. The B.C. government has prohibited nuclear power plants and banned uranium mining.
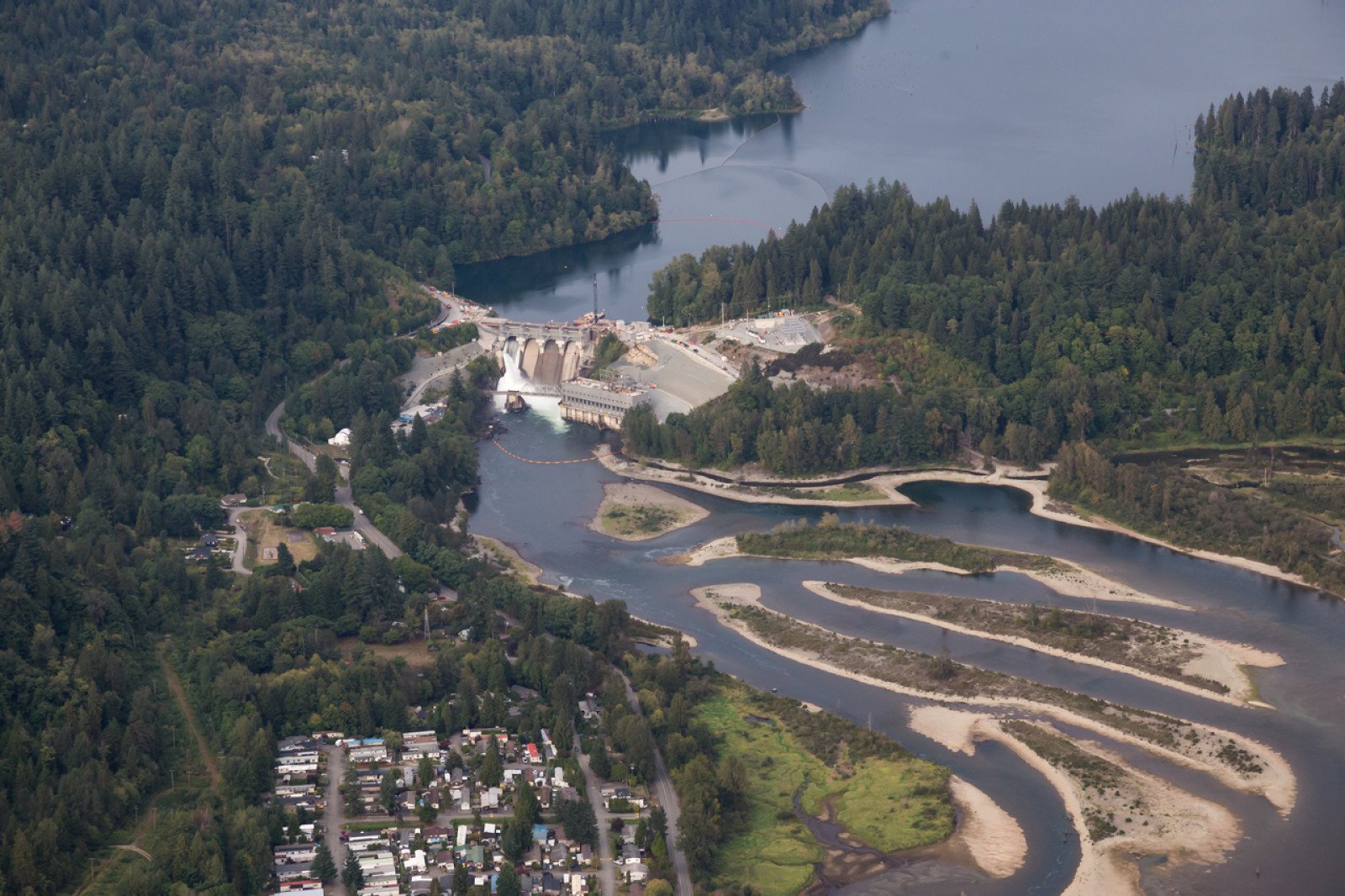
BC Hydro’s renewable electricity
BC Hydro uses the power of falling water to create clean, reliable and renewable electricity. However, despite being renewable it is essential we conserve electricity, as conservation is key to preventing further environmental impacts of increasing electricity demand. See here for more information.