Greenhouse effect experiment
See how things heat up with the greenhouse effect in a hands-on experiment.

Overview
What is the greenhouse effect? How does it impact Earth’s temperature? Students design a hands-on experiment about the greenhouse effect and Earth’s changing climate.
Instructions
What you'll need
- “Greenhouse effect” worksheet
- Laptops or other devices
- Materials available to each group:
- Two large clear containers (2L plastic bottles, large jars, bowls)
- Two thermometers
- Scissors
- Plastic wrap or clear plastic bags
- Rubber bands or strings
- Black construction paper
- Ice cubes
- Heat lamp
What do you know about the greenhouse effect?
- Ask students what they know about the greenhouse effect. Give them a few minutes to think on their own, then share ideas with a partner and discuss as a class.
- Show the image below to your class:
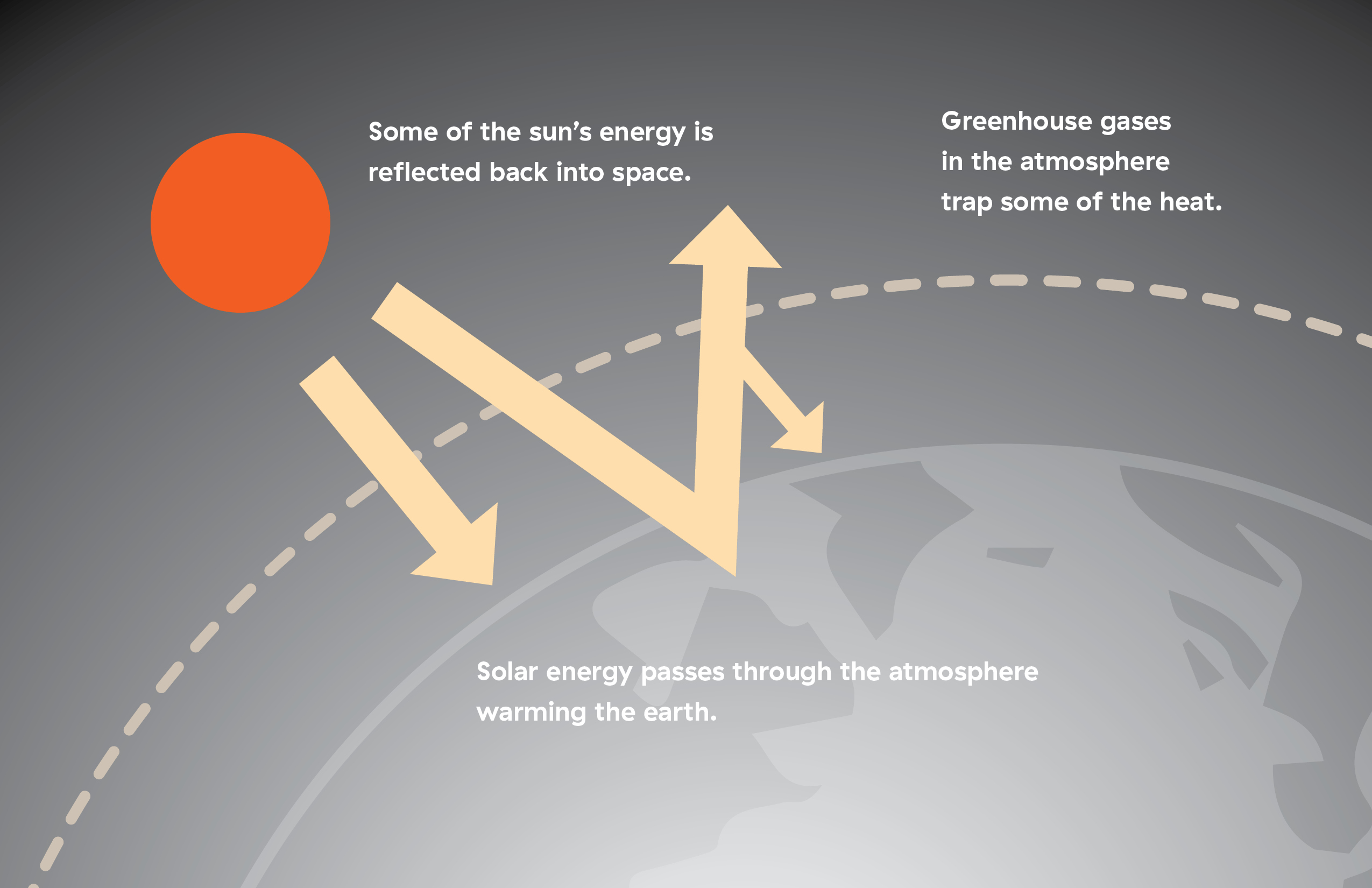
- Earth’s atmosphere has always acted like a greenhouse to trap in some of the heat energy from the sun, just like a greenhouse. Without the natural greenhouse effect, the Earth would be too cold for life to exist.
- Gases in the atmosphere provide the greenhouse effect. These gases are known as greenhouse gases (e.g. carbon dioxide, water vapour, nitrous oxide, methane).
- As greenhouse gas levels increase, more heat is trapped on Earth, causing a gradual increase in the overall temperature. This is known as global warming.
Design an experiment
- Divide students into small groups for the experiment. Students challenge themselves to design an experiment about the greenhouse effect using the materials provided.
- Each group should come up with a question about the greenhouse effect and then design an experiment to help answer it; or you could decide on a question as a class.
- A simple question could be “How does the greenhouse effect impact temperature?”
- Share ideas as a class.
- Experiment ideas:
- Cover one of the containers with plastic wrap to represent increasing greenhouse gases. Have thermometers in both containers and use a heat lamp as the sun.
- Wrap one of the containers with black construction paper to represent increasing greenhouse gases. Have thermometers in both containers and use a heat lamp as the sun.
- Have one container with ice and the other with black construction paper lining the inside to represent the effect of melting ice from the increasing temperature, etc. Have thermometers in both containers and use a heat lamp as the sun.
- Give each student a “Greenhouse effect” worksheet.
- Review the last page of the worksheet and remind your students to think about ways they’re developing competencies in this activity.
- In their groups, set up and start their experiment. Allow at least 30 minutes for observations.
- Have students work in groups and discuss questions, but complete their own worksheet.
- Circulate to help answer questions, facilitate discussion and assess competency development.
Reflection and connection
- Debrief. Have groups share their experiment results.
- What worked well? What was challenging? What would they do differently?
- Extend learning with a discussion:
- Share ideas about how the experiments connect to the real world.
- How do increasing greenhouse gases affect Earth’s climate?
- What do you think the role of humans has been in increasing the levels of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere?
Modify or extend this activity
- Have students conduct further research about questions of interest related to climate change and greenhouse gases. Have them create a Kahoot about climate change. You can check these resources:
Curriculum Fit
Grade 7 Science
Big idea
- Earth and its climate have changed over geological time
Content
- Evidence of climate change over geological time and the recent impact of humans
Curricular competencies
Questioning and predicting
- Make predictions about the findings of their inquiry
Planning and conducting
- Collaboratively plan a range of investigation types, including field work and experiments, to answer their questions or solve problems they have identified
- Measure and control variables (dependent and independent) through fair tests
- Observe, measure, and record data (qualitative and quantitative), using equipment, including digital technologies, with accuracy and precision
Processing and analyzing data and information
- Seek patterns and connections in data from their own investigations and secondary sources
Evaluating
- Identify possible sources of error and suggest improvements to their investigation method
- Consider social, ethical, and environmental implications of the findings from their own and others’ investigations
Applying and innovating
- Transfer and apply learning to new situations
Assessments
- Observe and assess students throughout the activity to assess competency development.
- Assess content understanding and self-reflection using the “Greenhouse effect” worksheet.
Teaching Notes
Greenhouse effect
The greenhouse effect is a natural process, keeping the Earth warm enough for life to exist. Greenhouse gases in the atmosphere, including carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide and water vapour, trap heat from the sun. The atmosphere acts like the glass in a greenhouse. Most scientists believe the Earth is getting warmer because of greenhouse gas emissions from human activities, in particular the burning of fossil fuels for things like manufacturing, transportation and power.










