Solving Ohm’s Law
Extend your knowledge of the relationship between voltage, current, and resistance.

Overview
Your students extend their understanding of Ohm’s Law by doing calculations with voltage, current, and resistance data.
Instructions
What you'll need
- Whiteboard or blackboard
- "Solving Ohm's Law" slideshow
- "Solving Ohm's Law" worksheet for each student
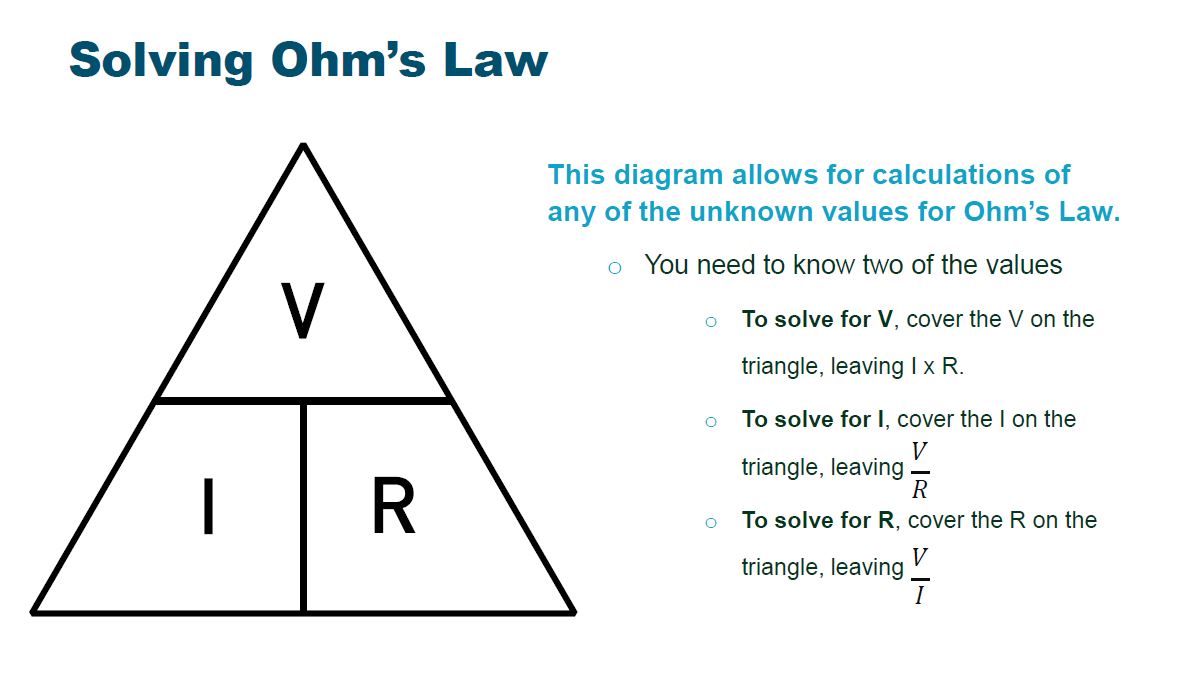
Ohm's Law triangle
- Go through the slideshow with the class.
- Show the students the triangle graphic from the slideshow. Ohm’s Law triangle illustrates the relationships between voltage (V), current (I) and resistance (R). Explain to the students how the triangle can be used to calculate unknown values. Simply cover the value you are looking for, and complete the related mathematical operation (either division or multiplication).
- Write this example on the whiteboard:
- If a circuit has a current (I) of 3 A, and its resistance (R) is 4 Ω, what is the voltage (V) of the circuit? You know that I = 3 A and R = 4 Ω, but you don’t know the value of V. Cover the V in the graphic, replace the I with 3 A and the R with 4 Ω; then multiply: 3 x 4 = 12. The voltage (V) equals 12 V.
- To determine resistance when V = 15 V and I = 3 A, cover the R and replace the V with 15 and A with 3. Then divide: 15 / 3 = 5. The resistance is 5 Ω.
- Work through these sample questions as a class:
- Find R when V = 9 V and I = 3 A.
- Find V when R = 100 Ω and I = 12 A.
- Find I when V = 12 V and R = 10 Ω.
- Have students work individually or in small groups to complete the “Solving Ohm’s Law” worksheet.
- As a class, review the Ohm’s Law triangle and answer any questions. Assist students as they complete the worksheet. Address any common misunderstandings or challenges with the problems.
Modify or extend this activity
- Review your students’ conversion of mA to A. There are 1,000 mA in one A. A simple way to convert is to move the decimal three places to the left.
- Check out "Exploring Ohm’s Law", "Introducing resistance" and "Investigating resistance" for more activities about resistance and Ohm’s Law.
Curriculum Fit
Grade 9 Science
Content
- Voltage, current and resistance
- Circuits
Curricular competencies
Questioning and predicting
- Demonstrate a sustained intellectual curiosity about a scientific topic or problem of personal interest
- Make observations aimed at identifying their own questions, including increasingly complex ones, about the natural world
Planning and conducting
- Collaboratively and individually plan, select, and use appropriate investigation methods, including field work and lab experiments, to collect reliable data (qualitative and quantitative)
- Select and use appropriate equipment, including digital technologies, to systematically and accurately collect and record data
- Ensure that safety and ethical guidelines are followed in their investigations
Processing and analyzing data and information
- Seek and analyze patterns, trends, and connections in data, including describing relationships between variables (dependent and independent) and identifying inconsistencies
- Analyze cause-and-effect relationships
Evaluating
- Evaluate their methods and experimental conditions, including identifying sources of error or uncertainty, confounding variables, and possible alternative explanations and conclusions
- Describe specific ways to improve their investigation methods and the quality of the data
Applying and innovating
- Transfer and apply learning to new situations
- Generate and introduce new or refined ideas when problem solving
Communicating
- Formulate physical or mental theoretical models to describe a phenomenon
Assessments
“Solving Ohm’s Law” worksheet answer key:
1. A smartphone with a resistance of 35 ohms has a current of 0.25 amps flowing through it. Sketch a circuit diagram and calculate how many volts supply the smart phone.
- V= I x R
- = 0.25 A x 35 Ω
- = 8.75 V
2. A 120-volt power source supplies a computer with a resistance of 210 ohms. What is the current flow of the circuit?
- I = V/R
- = 120 V/ 210 Ω
- = 0.57 A
3. Calculate the resistance of the following circuit diagram:
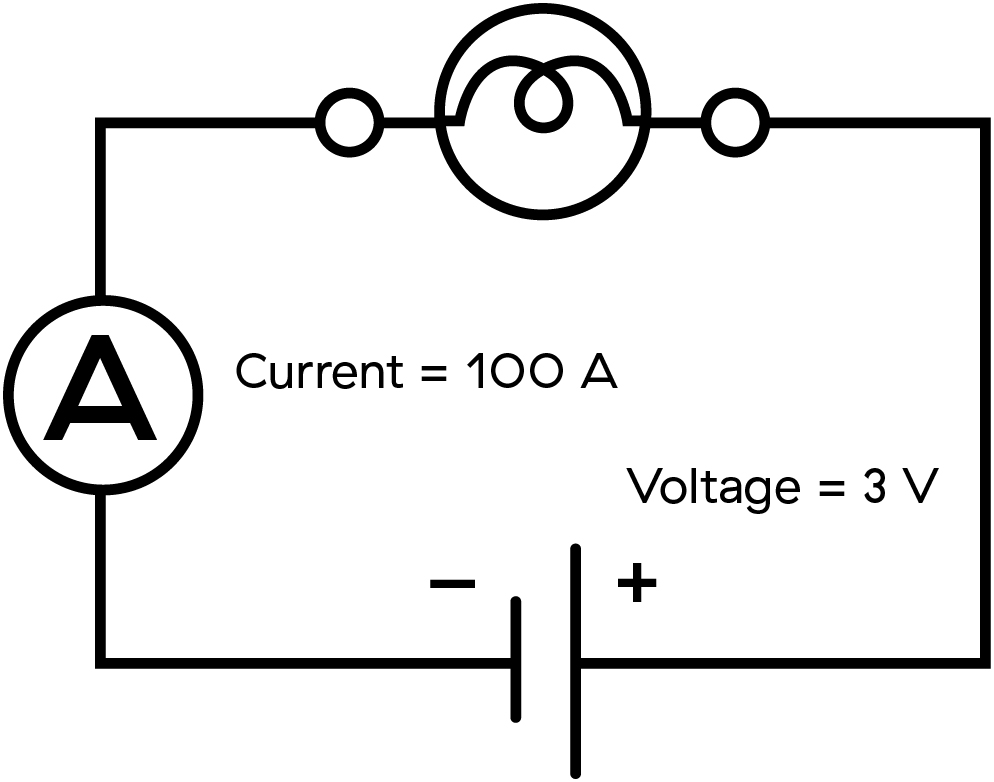
- R= V/I
- = 3 V/ 100 A
- = 0.03 Ω
4. What amount of voltage would you need to run a current of 1.2 amps through a 250-ohm resistor?
- V = I x R
- = 1.2 A x 250Ω
- = 300V
5. Using the given variables, calculate the unknown value:
- a. V = 10 V R = 5 Ω I = 2 A
- b. V = 3.5 V R = 10 Ω I = 0.35 A or 350 mA
- c. V = 10 V I = 2 A R = 5 Ω
- d. V = 3.5 V I = 0.5 A R = 7 Ω
- e. I = 11 A R= 3 Ω V = 33 V
- f. I = 7 A R = 4.5 Ω V = 31.5 V
Teaching Notes
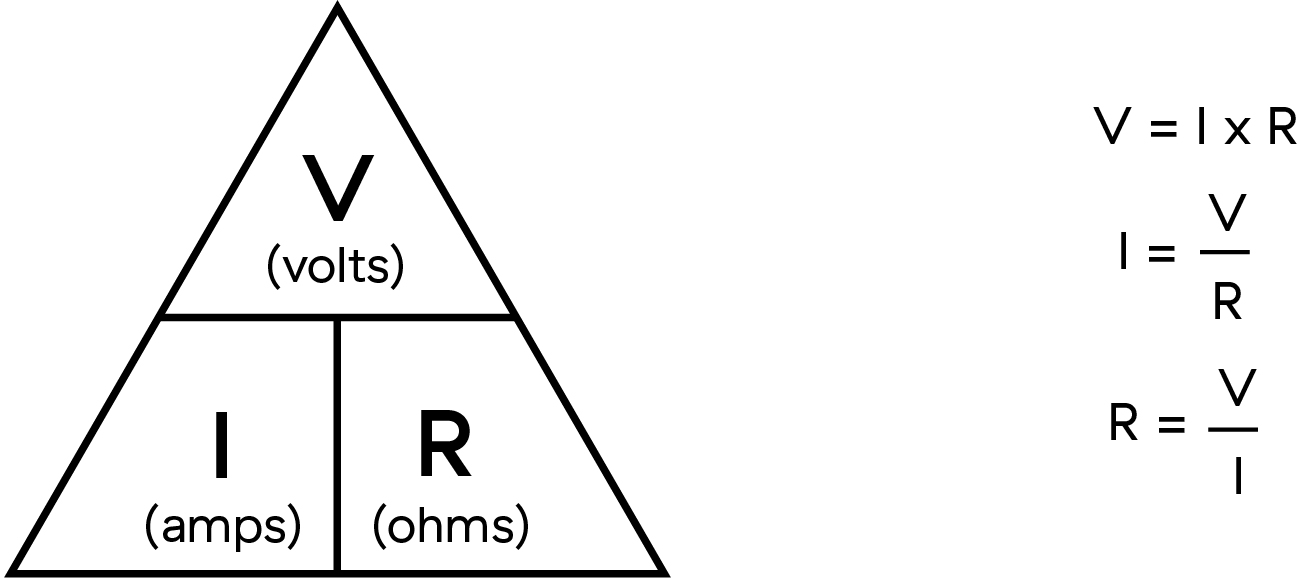
Ohm’s Law represents the relationship between voltage and current. It is usually represented mathematically:
- V = I x R
Where:
- V is the voltage (volts or V)
- I is the current (amperes or A)
- R is the resistance (ohms or Ω). Resistance is the ratio of voltage to current: V/I
It’s necessary to convert milliamperes (mA) to amperes (A) when using Ohm’s Law. There are 1,000 milliamperes (mA) in one ampere (A).