Introducing resistance
Learn how resistors in series and parallel circuits affect current and voltage.

Overview
You will demonstrate how the total resistance of a circuit increases when resistors are in series and decreases when resistors are in parallel.
Instructions
What you'll need
- Whiteboard
- 2 dry cell holders
- 2 dry cells
- 3 resistors, different ratings (100 to 1,000 ohms)
- Switch
- Connecting wires
- Voltmeter
- Ammeter
- “Introducing resistance” slideshow
Demonstrating resistance
- From the “Introducing resistance” slideshow, use slides 2 and 3 to introduce your students to resistors. Make sure they understand what resistors are and why they are used in electrical circuits. Show your students that the resistor values are colour coded.
Series circuit
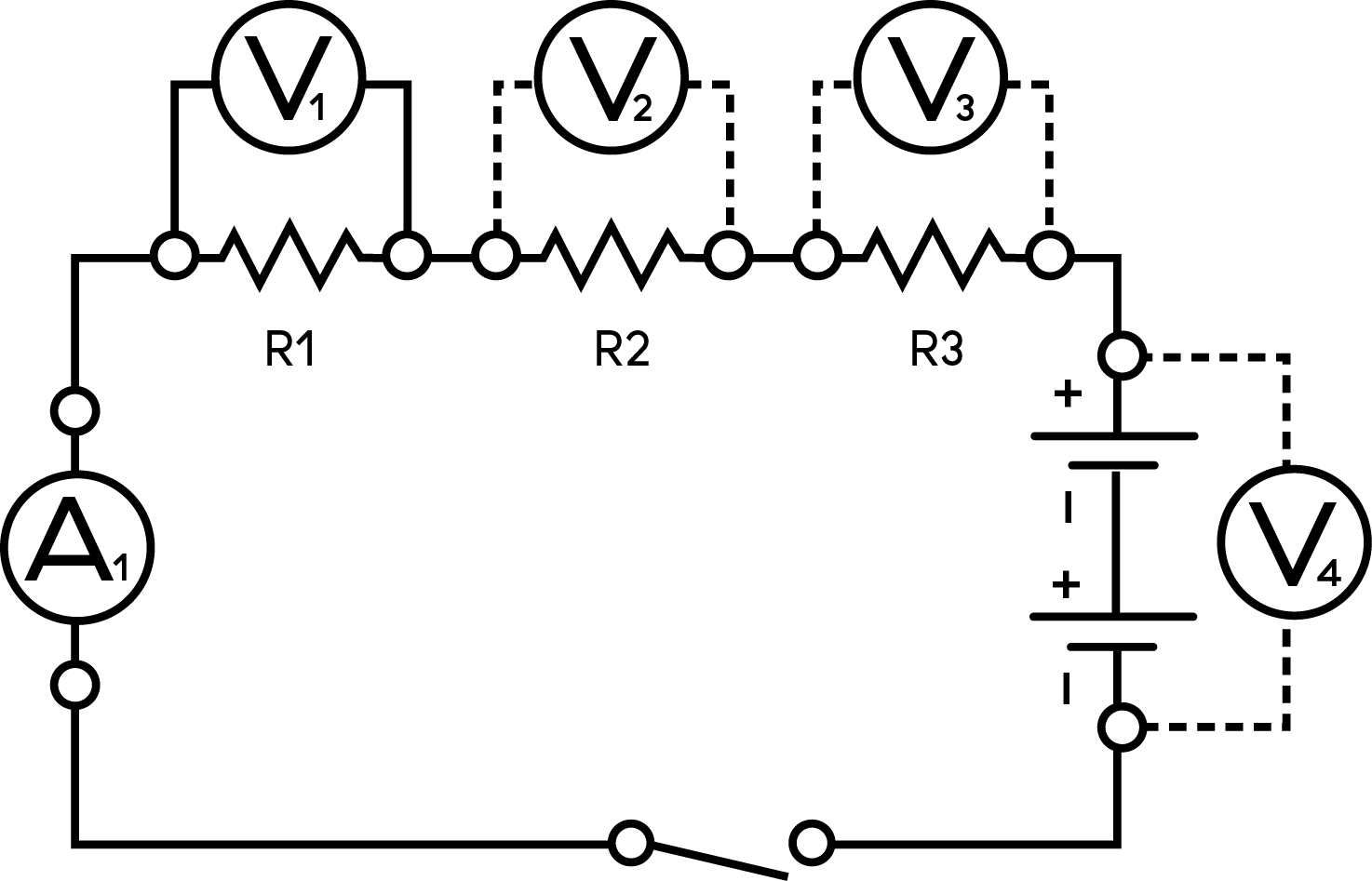
- Set up a series circuit. Demonstrate how to add one, two and three resistors.
- Have students draw the schematic of the circuit you created.
- Take measurements of the voltage (V1, V2, and V3) at each resistor, the total voltage across the dry cells (V4) and the current for the circuit (A1). Have your students record the data.
Parallel circuit
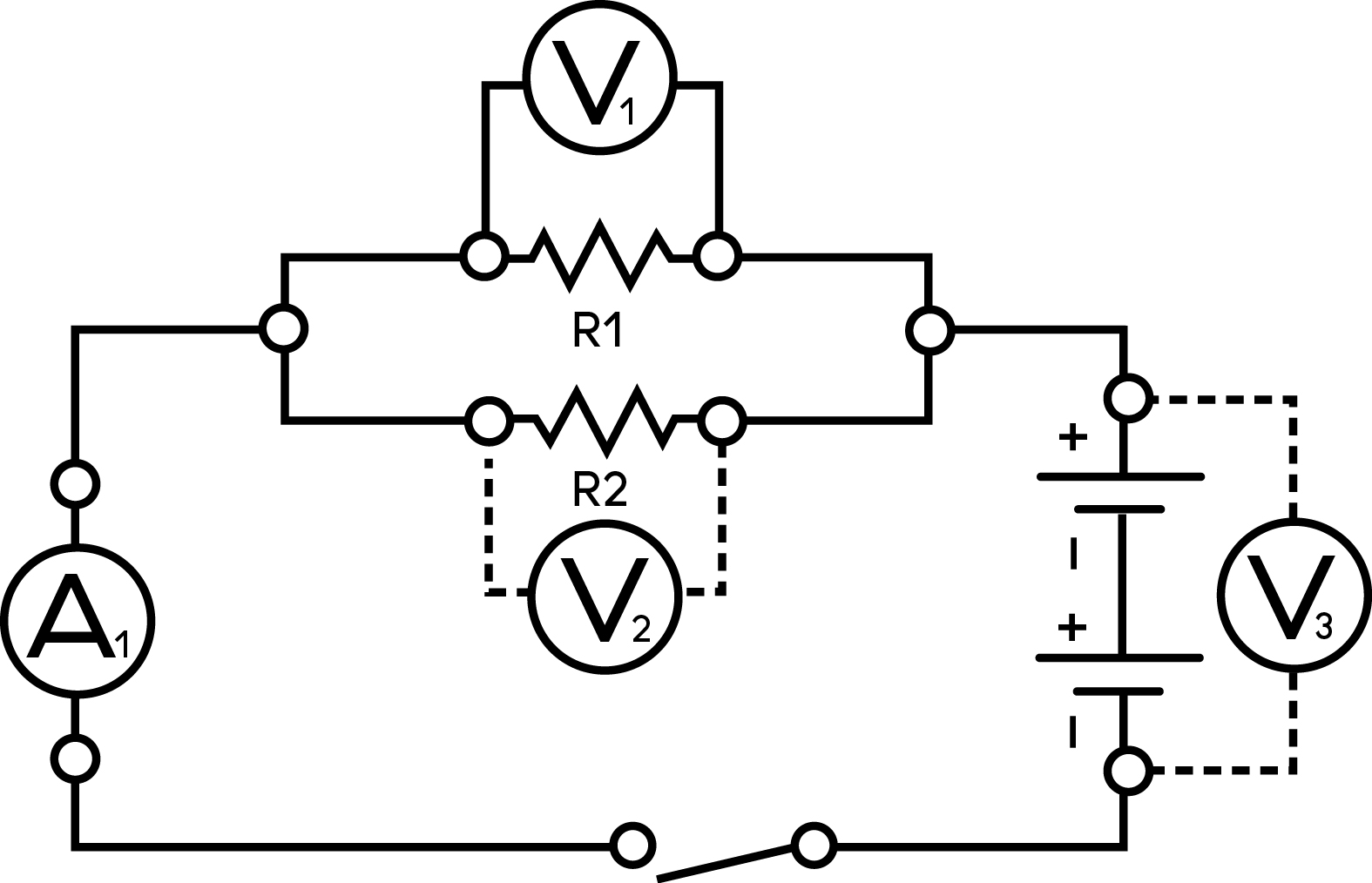
- Set up a parallel circuit.
- Have your students draw the schematic.
- Take measurements of the voltage at each of the two resistors (V1 and V2), the terminal voltage (V3), and the current (A1). Have your students record the data.
Thinking about the data
- Discuss any patterns the students observed in their voltage and current measurements.
- Use slides 4 and 5 from the “Introducing resistance” slideshow to summarize the key concepts.
Modify or extend this activity
- A waterslide analogy can help students visualize resistance in a circuit. If there are two or more parallel slides, more people can go down at once. Fewer people can go down a slide in series because only one person is allowed on at a time. This analogy can also be used to compare voltages. The height of each parallel slide is equal to the height of the ladder. The heights of two slides in series add up to make the total height larger than either of the slides on their own.
- “Exploring Ohm’s Law”, “Solving Ohm’s Law”and “Investigating resistance” activities extend understanding about resistance.
Curriculum Fit
Grade 9 Science
Content
- Voltage, current and resistance
- Circuits
Curricular competencies
Questioning and predicting
- Demonstrate a sustained intellectual curiosity about a scientific topic or problem of personal interest
Processing and analyzing
- Seek and analyze patterns, trends, and connections in data, including describing relationships between variables (dependent and independent) and identifying inconsistencies
- Analyze cause-and-effect relationships
Evaluating
- Evaluate their methods and experimental conditions, including identifying sources of error or uncertainty, confounding variables, and possible alternative explanations and conclusions
Applying and innovating
- Transfer and apply learning to new situations
- Generate and introduce new or refined ideas when problem solving
Communicating
- Formulate physical or mental theoretical models to describe a phenomenon
Assessments
Review your students’ sketches, assessing their schematic drawings and the accuracy of the data they recorded during the demonstrations. The answers for voltage and current data will vary according to how you conduct your demonstration, and depending on the charges in the dry cells.
Teaching Notes
Any electrical component with electrical resistance restricts the flow of electrons in a circuit and transforms electrical energy into other forms of energy.
A resistor is an electrical component with a specific resistance value. Resistors can be used to control current or to provide a specific voltage and current to other components in a circuit.
Resistor codes and values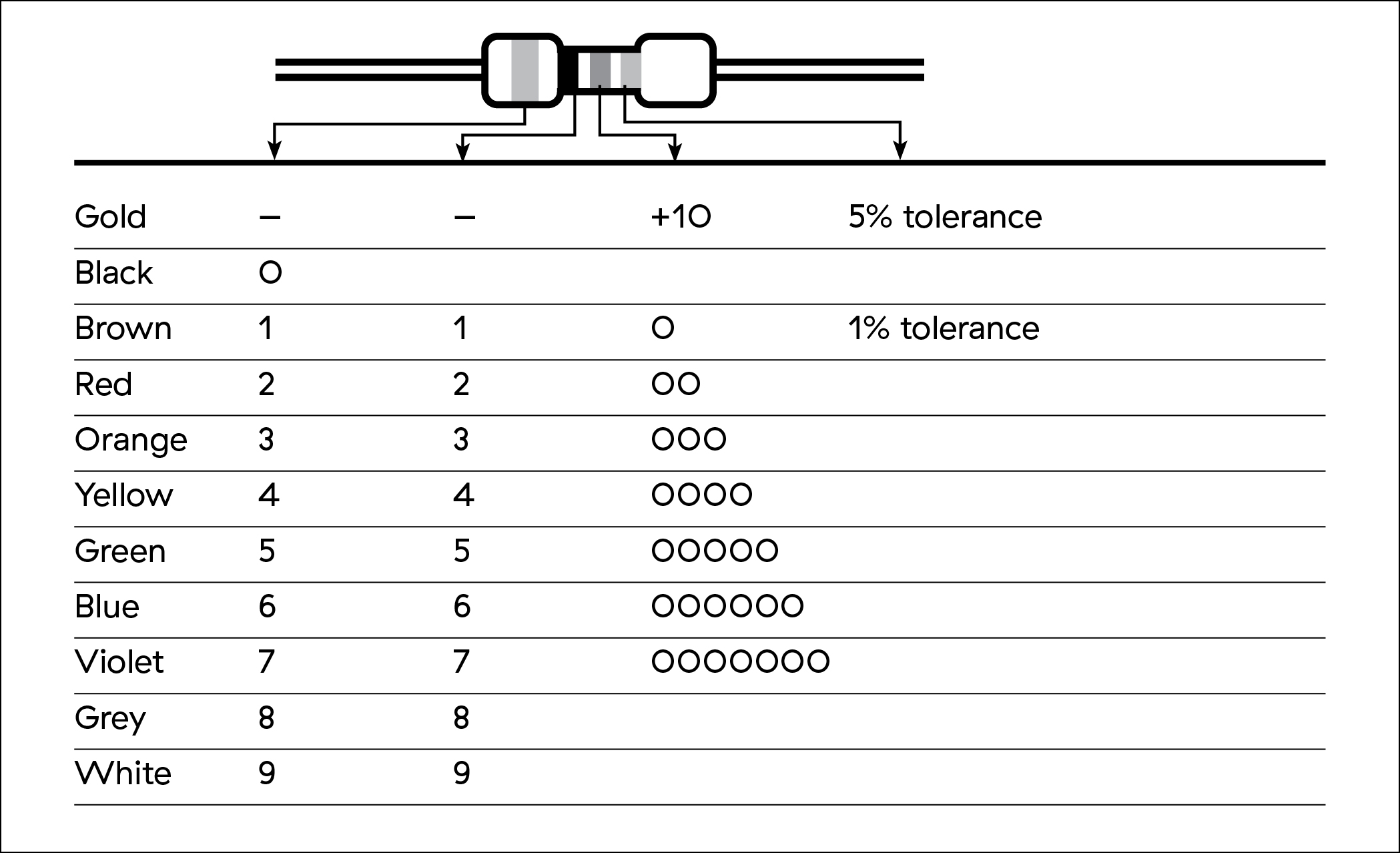
Students must understand how resistors are classified. For series circuits, if the resistors have the same resistance value, the voltage drop in each resistor will be the same. For parallel circuits, the current will be the same through each resistor, although each will be half of the total current. Using resistors with different values emphasizes how the voltage and current change in series and parallel circuits.
Students should be able to recognize the following relationships emerging from the data collected during their investigations:
- The total resistance of a circuit depends on the number of individual resistances.
- Increasing the number of resistors in a series circuit increases the total resistance and reduces the current.
- Increasing the number of resistors in a parallel circuit decreases the total resistance and increases the current flow by creating additional pathways.






